Environmental Impact of Food Production
Dear students,
you will work according to the following webquest and by the end you will be able to:
1. Explore Traditional and Modern Farming Practices
2. Assess Agricultural Environmental Impact by analyzing carbon, water and land footprints and compare these impacts across countries.
3. Discover how agriculture supports and influences the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for a better future.
Exploring Traditional and Modern Farmin Practices
Agriculture, both an art and a science, involves cultivating land for crop production and raising livestock. It is a vital element of Food Systems, acting as the main source of food production.
Within agriculture, traditional and modern farming practices play significant roles. Traditional agriculture typically relies on time-tested methods such as crop rotation, organic fertilization and diverse planting, which can enhance soil health and sustainability. In contrast, modern agriculture often employs advanced technologies, chemical fertilizers and monoculture practices to increase efficiency and yield. Both approaches influence the food system by determining how food is grown, processed and distributed. Integrating sustainable practices from both traditional and modern agriculture can help create a more resilient and environmentally friendly food system.
-
View the following presentation on ‘Traditional and Modern Farming Practices’ in Genial.ly and complete the accompanying quiz.
-
Read here about Anna, a 50-year-old farmer from a small Polish village, who operates a family-owned wheat farm using traditional methods. Discuss the environmental benefits and drawbacks of her traditional farming practices and explore possible improvements.
Assessing Agricultural Environmental Impact
Agriculture significantly impacts the environment by consuming large amounts of fresh water, contributing to water stress and pollution, driving climate change with around one-quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions and using half of the world's habitable land.
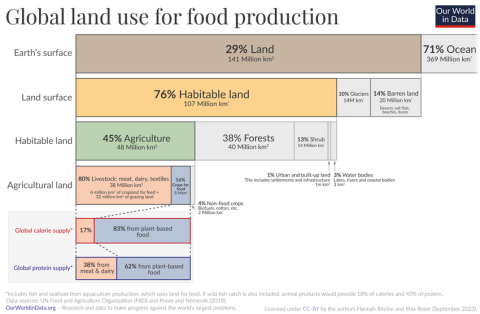
https://ourworldindata.org/images/published/Global-land-use-breakdown_850.png
The ecological footprint measures the environmental impact of human activities by quantifying the land and water needed to produce resources and manage waste. It includes factors like carbon emissions, water use, and land use. Agriculture significantly contributes to the ecological footprint through its extensive use of natural resources and impact on ecosystems. Key components include carbon, water, and land footprints.
-
The carbon footprint refers to the amount of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, released into the atmosphere as a result of agricultural activities. Modern practices, with heavy fossil fuel use and synthetic inputs, have a higher carbon footprint, while traditional methods generally produce fewer emissions.
-
The water footprint measures the total volume of fresh water used directly and indirectly by agricultural practices. Agriculture is a major consumer of water, especially through extensive irrigation systems in modern farming. This heavy reliance on irrigation can deplete water resources, particularly in arid regions and lead to water pollution from runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides. Traditional agriculture often uses rain-fed systems or small-scale irrigation, which are generally more sustainable but may face challenges in water-scarce areas.
-
The land footprint indicates the amount of land required for agricultural activities. Agriculture occupies about half of the world’s habitable land, making it a significant driver of land use change. Traditional agricultural systems, which include diverse crops and livestock, can help maintain soil fertility and biodiversity. However, improper management can lead to deforestation and land degradation. Modern agriculture, characterized by monocropping and large-scale farming, often results in habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and soil erosion.
By adopting sustainable practices, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and implementing efficient resource management, the agricultural sector can minimize its environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
-
You will be divided into three groups, each tasked with comparing the ecological footprint of two countries using the Global Footprint Network (https://data.footprintnetwork.org/#/compareCountries?type=EFCpc&cn=unde…):
-
Group 1- Compare Slovakia and Turkey
-
Group 2- Compare Greece and Slovakia
-
Group 3- Compare Turkey and Greece
2. In your group, examine the carbon, water, and land footprints of your assigned countries, making notes and taking screenshots as needed. Present your findings using Google Slides. Use the forum of the Twinspace’s related page to interact with your peers and agree on a common answer to the following questions in your presentation:
- How did the ecological footprints of the two countries you compared vary regarding carbon, water, and land use? What were the most notable differences you found?
- What factors do you believe contribute to these differences? Consider elements such as agricultural practices, climate, and economic development.
Useful links:
Mapping Agriculture's Impact on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG's)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), established by the United Nations in 2015, aim to eradicate poverty, safeguard the environment, and promote global peace and prosperity by 2030. The 17 interconnected SDGs emphasize the importance of balanced progress across social, economic, and environmental aspects. Agriculture is crucial in this effort, impacting and supporting many of the SDGs.
Useful link: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals
You will be divided in 4 groups. Your teacher will invite you to your group through the Coggle web2.0 tool to work on a mindmap.
Make online research for the SDGs and their relevance to agriculture. Focus on understanding how agriculture influences or supports each SDG.
Select 2-3 SDG Goals (each group). Create a mindmap in Coggle by starting from the central node ‘Agriculture’ and branching out relevant SDGs that are affected from Agriculture.https://coggle.it/diagram/Zp6PSpIiZZGAtTN_/t/-
For each SDG, add sub-branches to describe agricultural practices that impact each (positive and negative).
Present the mindmap in the classroom





